Large-Language Models (LLMs) provide a natural language interface capable of understanding user intent and delivering highly specific responses. The recent addition of "tooling" as a primary feature of LLMs has enabled them to retrieve information on-demand and trigger actions. This makes LLMs a viable natural language interface for various applications, including dashboards, ERPs, CRMs, BI systems, HRMS, SCM, and even customer-facing mobile and web applications. The Acorn Agent framework offers the infrastructure to build such LLM-powered applications by instrumenting LLMs with custom tooling in a safe, secure, and efficient manner. The Acorn Agent framework is open-source under the Apache 2.0 license.

Background
Large-Language Models are neural networks that process input text and incrementally generate intelligent responses. Advances in the size, topology, and training of LLMs increased their performance as conversational interfaces to near-human levels. To date, LLMs have been confined to chat and search applications, where they are trained on extensive corpora and augmented with query-specific information through methods such as RAG, FLARE, or text search.
The recent addition of "tooling" as a primary feature has broadened the applicability of LLMs. "Tooling" is a set of function definitions provided to the LLM either in-prompt or through training. The LLM can invoke these functions to retrieve information on demand (e.g., looking up the current weather) or trigger an external action (e.g., placing an order). This enables LLMs to interact with external systems and information outside the immediate user context. The LLM can invoke APIs, run database queries, execute computations, trigger UI updates, and more.
Tooling makes it possible to build conversational interfaces with LLMs for user facing applications that enable the user to interact naturally with the application through text or voice. However, integrating LLMs with custom tooling poses several challenges:
- Safety: LLMs are non-deterministic and prone to hallucinations, requiring careful validation and comprehensive observability to build safe and predictable applications.
- Security: LLMs are susceptible to injection attacks, necessitating safeguards to build secure applications that do not leak user information or secrets.
- Performance: LLMs are expensive to invoke and highly sensitive to prompt variation, requiring efficient function management to reduce context tokens and improve performance.
- Efficiency: The implementations of tools in chatbots or agents have to be written from scratch by the developers, needing to create the function definitions for the LLM, but also the function execution against an API or a Database.
Acorn Agent Framework

Acorn Agent is a framework for building LLM-powered applications through tooling. It provides the necessary infrastructure to instrument LLMs with custom tools, addressing challenges related to safety, security, performance, and efficiency:
- Safety: The framework validates function calls and supports auto-retry of invalid function invocations. It enables quick iteration of function definitions to improve accuracy and performance.
- Security: The framework sandboxes function calls through a defined "context," which includes sensitive function arguments (e.g., userid, sessionid, tokens) that are handled by the framework and not exposed to the LLM call stack.
- Performance: The framework gives developers full control over the context window construction to optimize cost and performance.
- Efficiency: The framework provides abstraction layers for managing tooling across many popular LLMs through a standard interface which reduces boilerplate code and custom instrumentation logic. while giving developers full control over context window constructionAt its core, Acorn Agent is a repository of tools that instruments and executes tools for LLMs using a JSON configuration format for semantic annotations, execution logic, and security context.
Additionally, Acorn Agent facilitates seamless integration of APIs, databases, libraries, and UI frontends as tooling for LLMs. Acorn Agent supports three types of tools:
- API: Invokes an external system through an API to retrieve information or trigger an action. The framework supports GraphQL, REST, and JDBC, giving the LLM access to internal microservices, external web services, databases, search engines, ERP systems, and more.
- Local: Invokes a local function to execute a library method or computation. This enables the LLM to execute mathematical or other computations where accuracy and determinism are important.
- Client: Forwards the tool call to the client or frontend to trigger a UI update, implemented as a function callback in JavaScript. This allows the LLM to customize the presentation of information to the user.
The Acorn Agent framework is open-source under the Apache 2.0 license. You can view the full source code, download it, and contribute to the project on Github.
Example LLM Application
To illustrate how the Acorn Agent framework works, consider building an LLM application providing a natural language interface for an online garden store. This application uses the same GraphQL API that the web application uses to place and retrieve customer orders. Additionally, it implements functions for unit conversions and React components on the frontend to display order status. With Acorn Agent, we can register all of these as tools within the framework, configure an LLM (such as OpenAI’s GPT, Llama3 on AWS Bedrock, or Google Gemini), and set up our system prompt for a friendly shopping assistant. When a user issues a request, the Acorn Agent framework manages the tools for the LLM.
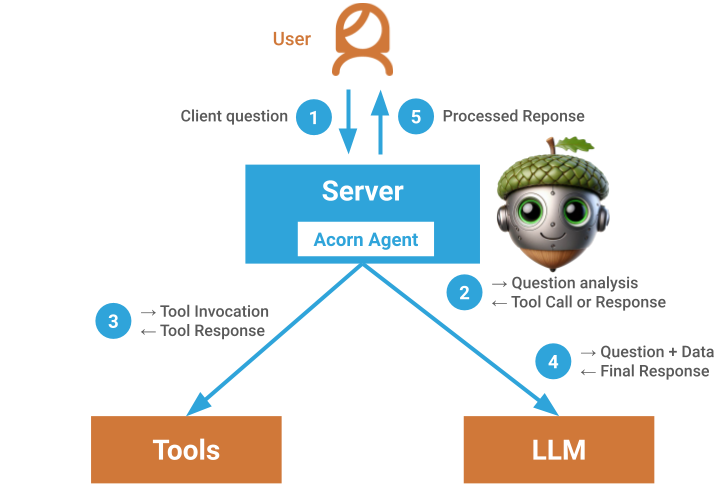
For example, suppose the user requests: "Order me fertilizer for 3 plots of lawn: 10x20 ft, 50x15 ft, and 30x35 ft. The same fertilizer I ordered last time." Acorn Agent injects the relevant tool definitions into the context and hands it to the LLM. The LLM processes the request and calls tools as follows:
- Look up the last orders for the fertilizer product ID and weight. Acorn Agent augments secure information from the user session, invokes the GraphQL API to retrieve the user’s last orders, and returns the information to the LLM. The LLM identifies which order was for fertilizer as well as the associated product id and weight.
- Convert the given measurements to total square footage and compute the number of bags needed for the fertilizer product based on the retrieved weight. Acorn Agent executes that tool by invoking a local function that implements the math and conversion. It then returns the number of bags to the LLM.
- Place the order for the computed number of fertilizer bags and retrieved product ID. Acorn Agent invokes the GraphQL API to place the order within the secure sandbox of the user session. The order details are returned to the LLM.
- Update the UI with the order information. Acorn Agent forwards that client function call with additional context to the UI to update the React component.
Acorn Agent handles all tool validations, sandboxing, invocations, and result propagations, allowing developers to focus on building tools and optimizing the context window.
Using Acorn Agent Framework
To experiment with Acorn Agent as a natural language interface for an existing API or database, you need only write tools and a configuration file—no coding required. Check out the examples for public APIs to get started. To build an LLM microservice or web application, you can include the Acorn Agent framework as a dependency in your Java, Scala, or Kotlin project. See the documentation for all the details. As an example, refer to the Spring Boot application using Acorn Agent to implement a ChatBot. If you have any questions, feedback, or would like to contribute, please join us on Slack. Currently, the Acorn Agent framework is limited to the JVM. We aim to support other programming environments soon.
Conclusion
Building natural language interfaces for user facing applications requires instrumenting LLMs with custom tooling. The open-source Acorn Agent framework provides the infrastructure to manage custom tooling for LLMs and ensures that application is safe, secure, and efficient.

